

Frontiers in Immunology, 4, 78.ĭmitriev, B. Peptidoglycan glycosyltransferase substrate mimics as templates for the design of new antibacterial drugs. BMC Microbiology, 11(1), 16.ĭerouaux, A., Sauvage, E., & Terrak, M. Induction kinetics of the Staphylococcus aureus cell wall stress stimulon in response to different cell wall active antibiotics. S., Heusser, R., Berger-Bächi, B., & McCallum, N. Probing teichoic acid genetics with bioactive molecules reveals new interactions among diverse processes in bacterial cell wall biogenesis. M., Hutter, B., Schaab, C., Moreno-Hagelsieb, G., & Brown, E. Microbial Cell Factories, 13(S1), S9.ĭ’Elia, M. Cell wall structure and function in lactic acid bacteria. Annual review of microbiology, 67, 313–336.Ĭhapot-Chartier, M. Wall teichoic acids of gram-positive bacteria. Synthesis of lipid II phosphonate analogues. Cytoplasmic steps of peptidoglycan biosynthesis. Journal of Endotoxin Research, 7(3), 167–202.īarreteau, H., Kovač, A., Boniface, A., Sova, M., Gobec, S., & Blanot, D. Invited review: Bacterial lipopolysaccharides and innate immunity.
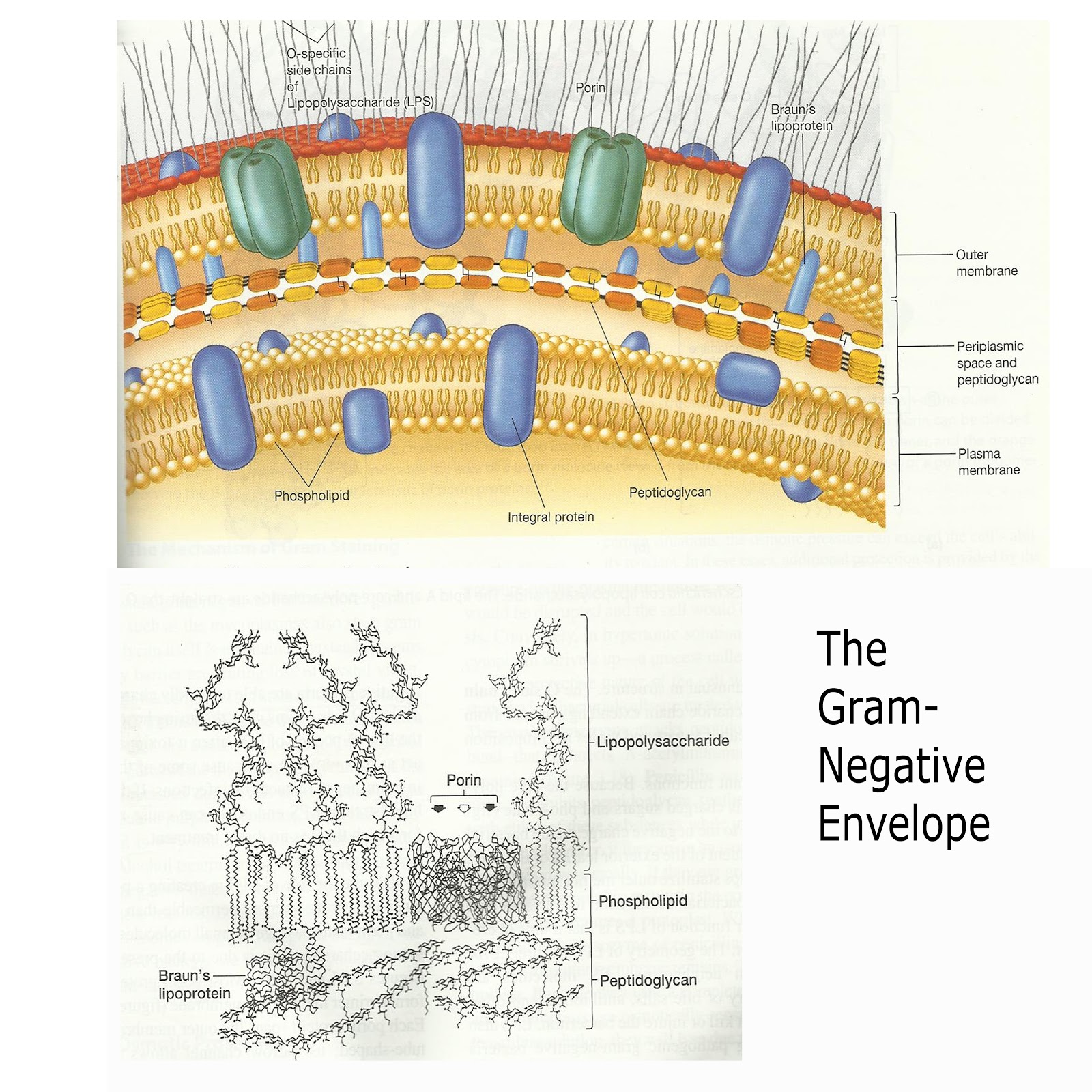
Detailed biosynthesis of cell wall along with various antibiotics that target specific steps during biosynthesis is discussed. These monomer saccharides proceed to synthesis of peptidoglycan involving several enzymatic steps. This is first converted to uridyl conjugate of N-acetyl glucosamine which converts to N-acetyl muramic acid by acetyl transferase reaction. Fructose-6-phosphate from glycolysis serves as precursor for initiating cell wall synthesis in the cytoplasm. Detailed cell wall biosynthetic pathway is described as four major steps involving several enzymes. The formation of this structure requires various enzymatic reactions acting on different substrates in different compartments of the cell. Different components of both gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial cell wall along with lipoprotein bilayer along with outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria are described. The bacterial cell wall is composed of peptidoglycan layer which has alternating units of N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) saccharide cross-linked in between by a peptide bridge.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
